EPO: In Vivo Process Requiring “Professional Medical Expertise” Excepted From Patentability
Recently the European Patent Office (EPO) has published Decision T 1695/07 – 3.3.07 of one of the Boards of Appeal dealing with the exception from patentability under Article 53(c) EPC. The catchword reads as follows:
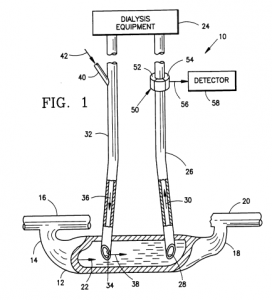
I. A blood manipulation process involving the continuous removal of blood from a patient, its subsequent flowing through a circulating line of an extracorporeal circuit and its re-delivery to the patient is a method of treatment of the human body by surgery excepted from patentability under Article 53(c) EPC. It does not belong to the kind of methods which should not be covered by the exception clause according to the “narrower understanding” suggested by the Enlarged Board of Appeal in decision G 1/07, because the process is not performed in a “non-medical, commercial environment” and cannot be considered as a “minor intervention” being performed on “uncritical parts of the body” (Reasons, 8 to 10).
II. Such an in vivo process requires “professional medical expertise” and belongs to the kind of interventions representing the “core of the medical profession’s activities”, even when performed by paramedical support staff (Reasons, 11).
III. Even when the process is carried out with the required medical professional care and expertise, it involves ”substantial health risks” for the patient. A health risk is considered to qualify as “substantial” whenever it goes beyond the side effects associated with treatments such as tattooing, piercing, hair removal by optical radiation, micro abrasion of the skin as mentioned in G 1/07. A factual analysis of absolute or relative risks and their likelihood of occurrence based on objective evidence is hardly feasible and should therefore not be required.
In the Decision the Board argues the claimed process does not fall under the “narrower understanding”, i.e. does not belong to the kind of methods which should not be covered by the exception clause according to the criteria developed in G 1/07 because of it comprises the steps of
- “continuously removing blood from a downstream location in the shunt (12) …” and
- “delivering the removed blood flowing in said circulating line by way of an outlet connected to an outlet side of said circulating line to an upstream location of said shunt, …”.
Furthermore and again according to the Board, It has been established that these steps are invasive and represent a substantial physical intervention on the body which requires professional medical expertise to be carried out and which entails a substantial health risk even when carried out with the required professional care and expertise. ccording to the established jurisprudence of the Boards of Appeal, a multi-step method falls under the exception clause of Article 53(c) EPC, if it includes at least one feature that constitutes a method step for the treatment of the human body by surgery. The possible technical contribution of the invention as mentioned by the proprietor appellants is not a criterion to be taken into consideration in this context.
Axel H. Horns
German & European Patent, Trade Mark & Design Attorney
The k/s/n/h::law blog
Some of the patent attorneys of the KSNH law firm have joined their efforts to research what is going on in the various branches of IP law and practice in order to keep themselves, their clients as well as interested circles of the public up to date. This blog is intended to present results of such efforts to a wider public.
Blog Archives
- November 2013 (2)
- October 2013 (1)
- September 2013 (1)
- August 2013 (2)
- July 2013 (3)
- June 2013 (5)
- March 2013 (5)
- February 2013 (4)
- January 2013 (5)
- December 2012 (5)
- November 2012 (5)
- July 2012 (5)
- June 2012 (8)
- May 2012 (5)
- April 2012 (3)
- March 2012 (4)
- February 2012 (5)
- January 2012 (6)
- December 2011 (12)
- November 2011 (9)
- October 2011 (9)
- September 2011 (4)
- August 2011 (7)
- July 2011 (4)
- June 2011 (1)
Blog Categories
- business methods (6)
- EPC (7)
- EPO (12)
- EU law (92)
- ACTA (8)
- CJEU (4)
- Comitology (1)
- competition law (2)
- Enforcement (6)
- EU Unified Patent Court (62)
- FTA India (1)
- TFEU (2)
- Trade Marks (5)
- European Patent Law (37)
- German Patent ACt (PatG) (1)
- German patent law (5)
- Germany (6)
- Pirate Party (3)
- International Patent Law (4)
- PCT (2)
- IP politics (10)
- licenses (2)
- Litigation (5)
- Patentability (7)
- Patents (12)
- Piratenpartei (2)
- Software inventions (10)
- Uncategorized (9)
- Unitary Patent (24)
- US Patent Law (4)
Comments
- kelle on Germany: Copyright Protection More Easily Available For Works Of “Applied Arts”
- Time Limits & Deadlines in Draft UPCA RoP: Counting The Days - KSNH Law - Intangible.Me on Wiki Edition of Agreement on Unified Patent Court Agreement (UPCA)
- Time Limits & Deadlines in Draft UPCA RoP: Counting The Days | ksnh::law on Wiki Edition of Agreement on Unified Patent Court Agreement (UPCA)
- Wiki Edition of Agreement on Unified Patent Cou... on Wiki Edition of Agreement on Unified Patent Court Agreement (UPCA)
- European Commission Takes Next Step Towards Legalising Software Patents in Europe | Techrights on EU Commission publishes Proposal of amendend Brussels I Regulation for ensuring Enforcement of UPC Judgements
Blogroll
- 12:01 Tuesday
- America-Israel Patent Law
- Anticipate This!
- AwakenIP
- BlawgIT
- BLOG@IPJUR.COM
- BP/G Radio Intellectual Property Podcast
- Broken Symmetry
- Class 46
- Director's Forum: David Kappos' Public Blog
- Gray on Claims
- I/P UPDATES
- IAM Magazine Blog
- Intellectual Property Intelligence Blog
- IP Asset Maximizer Blog
- IP CloseUp
- IP Dragon
- IP Watch
- IP Watchdog
- IPBIZ
- ipeg
- IPKat
- ITC 337 Law Blog
- Just a Patent Examiner
- K's Law
- MISSION INTANGIBLE
- Patent Baristas
- Patent Circle
- Patent Docs
- Patently Rubbish
- PatentlyO
- Patents Post-Grant
- Reexamination Alert
- SPICY IP
- Tangible IP
- The 271 Patent Blog
- The Intangible Economy
- THE INVENT BLOG®
- Think IP Strategy
- Tufty the Cat
- Visae Patentes
The KSNH blogging landscape


This blog and the German-language sister blog k/s/n/h::jur link to the two popular and privately run blogs IPJur und VisaePatentes and continue their work and mission with a widened scope and under the aegis of our IP law firm.
ksnhlaw on Twitter
- No public Twitter messages.
 KSNH::JUR Feed (german)
KSNH::JUR Feed (german)- Ist Verschlüsselung passé? September 6, 2013Auf verschiedenen Feldern beruflicher Praxis ist dafür zu sorgen, dass Kommunikation vertraulich bleibt. Die trifft beispielsweise für Ärzte zu, aber auch für Anwälte, darunter auch Patentanwälte. Einer der zahlreichen Aspekte, die in diesem Zusammenhang eine Rolle spielen, ist die Technik, um die Vertraulichkeit beruflicher Kommunikation sicherzustellen. Wa […]
- EU-Einheitspatent: Demonstrativer Optimismus und Zahlenmystik allerorten – Naivität oder politische Beeinflussung? June 26, 2013Nach mehreren vergeblichen Anläufen zur Schaffung eines EU-weiten Patentsystems wurde 1973 als Kompromiss das Europäische Patentübereinkommen unterzeichnet, welches unabhängig von der seinerzeit noch EWG genannten Europäischen Union System zur zentralisierten Patenterteilung mit nachgeordnetem Einspruchsverfahren durch das Europäische Patentamt schuf. Wie wi […]
- Moderne Zeiten oder: DPMA und Patentgericht streiten über die elektronische Akte April 25, 2013Bekanntlich hat das Deutsche Patent- und Markenamt (DPMA) im Jahre 2013 mit der rein technischen Fertigstellung der Einrichtungen zur elektronischen Akteneinsicht einen wichtigen Meilenstein seines Überganges von der Papierakte zur “elektronischen Akte” erreicht. Im DPMA werden aber bereits seit dem 01. Juni 2011 Patente, Gebrauchsmuster, Topografien und erg […]
- Gutachten zu Forschung, Innovation und technologischer Leistungsfähigkeit Deutschlands 2013 March 11, 2013Unter dem Datum vom 28. Februar 2013 ist die Bundestags-Drucksache 17/12611 veröffentlicht worden Sie trägt den Titel Unterrichtung durch die Bundesregierung - Gutachten zu Forschung, Innovation und technologischer Leistungsfähigkeit Deutschlands 2013. Die Bundesregierung legt dem Deutschen Bundestag seit dem Jahr 2008 […]
- 3D-Printing: Zum Filesharing von 3D-Modelldaten February 25, 2013In meiner kleinen zuvor angekündigten Reihe über rechtliche Aspekte des 3D Printing komme ich heute auf die Frage zu sprechen, ob die Hersteller von Gerätschaften es hinnehmen müssen, wenn Ersatztreile davon – vom Brillengestell über Smartphone-Gehäuseteile bis hin zu Rastenmähermotor-Abdeckungen – gescannt und die daraus […]
- Ist Verschlüsselung passé? September 6, 2013