 According to Chapter II PCT (International Preliminary Examination) the International Preliminary Examination Authority (IPEA) draws up the International Preliminary Examination Report (IPER) which is forwarded to the elected national patent Offices upon national phase entry. Since most national Offices use the IPER as a basis for their substantive examination, it is vital for the applicant that a positive IPER is established.
According to Chapter II PCT (International Preliminary Examination) the International Preliminary Examination Authority (IPEA) draws up the International Preliminary Examination Report (IPER) which is forwarded to the elected national patent Offices upon national phase entry. Since most national Offices use the IPER as a basis for their substantive examination, it is vital for the applicant that a positive IPER is established.
Based on Rule 66.4 PCT, reading
Additional Opportunity for Submitting Amendments or Arguments:
(a) If the International Preliminary Examining Authority wishes to issue one or more additional written opinions, it may do so, and Rules 66.2 and 66.3 shall apply.
(b) On the request of the applicant, the International Preliminary Examining Authority may give him one or more additional opportunities to submit amendments or arguments.
the EPO now announced an important procedural change for international applications entering Chapter II PCT before the EPO functioning as IPEA (see Notice from the EPO dated 31 August 2011). According to that revised practice, the EPO obtains discretion to issue additional written opinions before establishing the IPER, either on its own initiative or upon applicant’s request. This will give applicants more control and influence and better chances to enter the national phase with a positive IPER.
Yesterday the EPO News channel reported on a “renewed commitment to cost-efficient European patents” by the EPO and the European Commission. As nobody really had the slightest doubts on the continued and strong support by the project’s two main driving forces, this “news” does not sound that confident and persuasive as it apparenty was intended.
I cannot help, but to me it sounds more like political PR language or even autosuggestion if the President of the EPO, Benoît Battistelli, and the European Commissioner for the Internal Market and Services, Michel Barnier, jointly confess that “the unitary patent is [...] expected to simplify procedures and lower the costs for applicants by up to 70%“.
Fees for International Applications Change as of 1 September 2011
As of 1 September 2011 the fees for international (PCT) applications will change (see EPO Notification of EPO of 3 Augst 2011) as follows:
- International filing fee: from EUR 999 to EUR 1 088
- Fee per sheet in excess of 30: EUR 11 to EUR 12
- Reductions (under the Schedule of Fees, item 4):
- Electronic filing (the request being in character coded format) from EUR 150 to EUR 164
- Electronic filing (in character coded format) from EUR 225 to EUR 245
- Handling fee: from EUR 150 to EUR 164
The fees for international applications are calculated in Swiss Francs (CHF). The fee change is due to another amendment (after that of 1 January 2011) of the equivalent amounts in EUR by the International Bureau (see Official Notice in PCT Gazette of July 2011 (p. 94).
Back in September 2010 the EPO-sponsored 15th European Patent Judge’s Symposium took place in Lisbon, where the judges discussed developments in European patent law. The symposium was attended by 120 patent judges from Europe and guests from the USA and Japan. A big issue of course was the EU patent and the related litigation system, but the related discussion is now meaningless in view of the recent developments in this regard. But there were other interesting topics discussed as well.
For instance, in a working session on “Patentability of Computer implemented inventions”, Mr. Dai Rees – Chairman of an EPO appeal board and member of the Enlarged Board of Appeals that issued the G3/08 opinion – outlined the developments of the respective EPO case law. His contribution is documented in an article in the conference proceedings: Special edition 1/2011 of EPO Office Journal (PDF, 5 MB), pp. 93 to 102. The below summary reflects my personal observations and understanding of Mr. Rees presentation and also contains some individual flavours and thoughts.
Relevant Provisions: As a reminder, the provisions of the EPC to be considered for computer programs or technicality issues not only involve Art 52 EPC (“programs for computers as such“), but also Articles 18, 19, 21, 22 and Rules 42(1)(a), (c), 43(1) and 44 EPC, which use the term “technical” in different contexts. Further, in the EPC 2000 revision, Art 52(1) EPC was clarified in that patents shall be granted for inventions “in all fields of technology”, which, however, was regarded as a clarification rather than a substantive amendment of the Convention.
Amazon’s One-Click Patent in Europe and Elsewhere
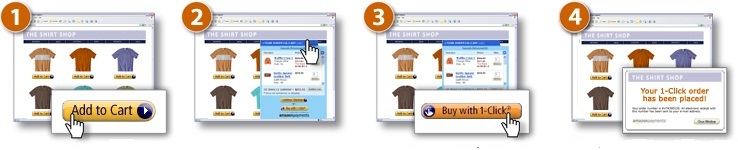 Amazon’s so called “One-Click Patent” is one of the most controversially discussed software inventions ever. The term, which nowadays is used as a cipher for a prototypical business method patent, was originally coined for US 5,960,411 titled “method and system for placing a purchase order via a communications network” (filed 12 Sep 2007, granted 28 Sep 1999; pdf), which has been enforced against competitor Barnes & Noble and licensed to Apple.
Amazon’s so called “One-Click Patent” is one of the most controversially discussed software inventions ever. The term, which nowadays is used as a cipher for a prototypical business method patent, was originally coined for US 5,960,411 titled “method and system for placing a purchase order via a communications network” (filed 12 Sep 2007, granted 28 Sep 1999; pdf), which has been enforced against competitor Barnes & Noble and licensed to Apple.
The respective teaching enables easy Internet shopping in that a customer visits a website, enters address and payment information and is associated with an identifier stored in a “cookie” in his client computer. A server is then able to recognize the client by the cookie and to retrieve purchasing information related to the customer, who thus can buy an item with a “single click”.
EP Parent Application: The first “1-click” application in Europe, EP 0 909 381 A2, related to an Internet-based customer data system and claimed a “method for ordering an item using a client system“. The application has been withdrawn on 08 June 2001 in view of approaching oral proceedings that had been summoned by the Examining Division with a negative preliminary opinion saying that the claimed teaching was not inventive over prior art document D3 (Baron C: “Implementing a Web shopping cart”, Dr. Dobbs Journal, Redwood City, CA, 01.09.1997). During the proceedings, Dutch Internet bookseller BOL.COM supported the Examining Division by a number of third party observations according to Art. 115 EPC, all of which pointing the Examining Division to the relevance of D3 (see e.g. here or here).
I. RECENT CASE LAW
In the past two years we have seen a number of quite interesting decisions of the German Federal Court of Justice (Bundesgerichtshof; BGH) dealing with patent-eligibility of software-related inventions.
The first decision in the row was X ZB 22/07 („Steuerung für Untersuchungsmodalitäten“, “Control of Examination Modalities”) of 20 January 2009, in which the BGH analysed the circumstances under which an embedded software represents statutory subject-matter (see comments). In this decision the BGH sketched a two-step approach to examine whether or not an invention is sufficiently “technical” to qualify for patent eligibility:
- Is the subject-matter a “technical invention” as required by § 1 I PatG ?
- Does the invention fall under the exclusion of a “computer programs as such” as requited by § 1 III No. 3, IV PatG ?
An additional third step completes the examination scheme:
- Do the technical features render the invention novel and inventive over prior art?
The k/s/n/h::law blog
Some of the patent attorneys of the KSNH law firm have joined their efforts to research what is going on in the various branches of IP law and practice in order to keep themselves, their clients as well as interested circles of the public up to date. This blog is intended to present results of such efforts to a wider public.
Blog Archives
- November 2013 (2)
- October 2013 (1)
- September 2013 (1)
- August 2013 (2)
- July 2013 (3)
- June 2013 (5)
- March 2013 (5)
- February 2013 (4)
- January 2013 (5)
- December 2012 (5)
- November 2012 (5)
- July 2012 (5)
- June 2012 (8)
- May 2012 (5)
- April 2012 (3)
- March 2012 (4)
- February 2012 (5)
- January 2012 (6)
- December 2011 (12)
- November 2011 (9)
- October 2011 (9)
- September 2011 (4)
- August 2011 (7)
- July 2011 (4)
- June 2011 (1)
Blog Categories
- business methods (6)
- EPC (7)
- EPO (12)
- EU law (92)
- ACTA (8)
- CJEU (4)
- Comitology (1)
- competition law (2)
- Enforcement (6)
- EU Unified Patent Court (62)
- FTA India (1)
- TFEU (2)
- Trade Marks (5)
- European Patent Law (37)
- German Patent ACt (PatG) (1)
- German patent law (5)
- Germany (6)
- Pirate Party (3)
- International Patent Law (4)
- PCT (2)
- IP politics (10)
- licenses (2)
- Litigation (5)
- Patentability (7)
- Patents (12)
- Piratenpartei (2)
- Software inventions (10)
- Uncategorized (9)
- Unitary Patent (24)
- US Patent Law (4)
Comments
- kelle on Germany: Copyright Protection More Easily Available For Works Of “Applied Arts”
- Time Limits & Deadlines in Draft UPCA RoP: Counting The Days - KSNH Law - Intangible.Me on Wiki Edition of Agreement on Unified Patent Court Agreement (UPCA)
- Time Limits & Deadlines in Draft UPCA RoP: Counting The Days | ksnh::law on Wiki Edition of Agreement on Unified Patent Court Agreement (UPCA)
- Wiki Edition of Agreement on Unified Patent Cou... on Wiki Edition of Agreement on Unified Patent Court Agreement (UPCA)
- European Commission Takes Next Step Towards Legalising Software Patents in Europe | Techrights on EU Commission publishes Proposal of amendend Brussels I Regulation for ensuring Enforcement of UPC Judgements
Blogroll
- 12:01 Tuesday
- America-Israel Patent Law
- Anticipate This!
- AwakenIP
- BlawgIT
- BLOG@IPJUR.COM
- BP/G Radio Intellectual Property Podcast
- Broken Symmetry
- Class 46
- Director's Forum: David Kappos' Public Blog
- Gray on Claims
- I/P UPDATES
- IAM Magazine Blog
- Intellectual Property Intelligence Blog
- IP Asset Maximizer Blog
- IP CloseUp
- IP Dragon
- IP Watch
- IP Watchdog
- IPBIZ
- ipeg
- IPKat
- ITC 337 Law Blog
- Just a Patent Examiner
- K's Law
- MISSION INTANGIBLE
- Patent Baristas
- Patent Circle
- Patent Docs
- Patently Rubbish
- PatentlyO
- Patents Post-Grant
- Reexamination Alert
- SPICY IP
- Tangible IP
- The 271 Patent Blog
- The Intangible Economy
- THE INVENT BLOG®
- Think IP Strategy
- Tufty the Cat
- Visae Patentes
The KSNH blogging landscape


This blog and the German-language sister blog k/s/n/h::jur link to the two popular and privately run blogs IPJur und VisaePatentes and continue their work and mission with a widened scope and under the aegis of our IP law firm.
ksnhlaw on Twitter
- No public Twitter messages.
 KSNH::JUR Feed (german)
KSNH::JUR Feed (german)- Ist Verschlüsselung passé? September 6, 2013Auf verschiedenen Feldern beruflicher Praxis ist dafür zu sorgen, dass Kommunikation vertraulich bleibt. Die trifft beispielsweise für Ärzte zu, aber auch für Anwälte, darunter auch Patentanwälte. Einer der zahlreichen Aspekte, die in diesem Zusammenhang eine Rolle spielen, ist die Technik, um die Vertraulichkeit beruflicher Kommunikation sicherzustellen. Wa […]
- EU-Einheitspatent: Demonstrativer Optimismus und Zahlenmystik allerorten – Naivität oder politische Beeinflussung? June 26, 2013Nach mehreren vergeblichen Anläufen zur Schaffung eines EU-weiten Patentsystems wurde 1973 als Kompromiss das Europäische Patentübereinkommen unterzeichnet, welches unabhängig von der seinerzeit noch EWG genannten Europäischen Union System zur zentralisierten Patenterteilung mit nachgeordnetem Einspruchsverfahren durch das Europäische Patentamt schuf. Wie wi […]
- Moderne Zeiten oder: DPMA und Patentgericht streiten über die elektronische Akte April 25, 2013Bekanntlich hat das Deutsche Patent- und Markenamt (DPMA) im Jahre 2013 mit der rein technischen Fertigstellung der Einrichtungen zur elektronischen Akteneinsicht einen wichtigen Meilenstein seines Überganges von der Papierakte zur “elektronischen Akte” erreicht. Im DPMA werden aber bereits seit dem 01. Juni 2011 Patente, Gebrauchsmuster, Topografien und erg […]
- Gutachten zu Forschung, Innovation und technologischer Leistungsfähigkeit Deutschlands 2013 March 11, 2013Unter dem Datum vom 28. Februar 2013 ist die Bundestags-Drucksache 17/12611 veröffentlicht worden Sie trägt den Titel Unterrichtung durch die Bundesregierung - Gutachten zu Forschung, Innovation und technologischer Leistungsfähigkeit Deutschlands 2013. Die Bundesregierung legt dem Deutschen Bundestag seit dem Jahr 2008 […]
- 3D-Printing: Zum Filesharing von 3D-Modelldaten February 25, 2013In meiner kleinen zuvor angekündigten Reihe über rechtliche Aspekte des 3D Printing komme ich heute auf die Frage zu sprechen, ob die Hersteller von Gerätschaften es hinnehmen müssen, wenn Ersatztreile davon – vom Brillengestell über Smartphone-Gehäuseteile bis hin zu Rastenmähermotor-Abdeckungen – gescannt und die daraus […]
- Ist Verschlüsselung passé? September 6, 2013








